pdf musculoskeletal system
- by zachery

The musculoskeletal system‚ comprising bones‚ muscles‚ joints‚ and connective tissues‚ enables movement‚ provides structural support‚ and protects internal organs. It plays a vital role in maintaining posture‚ facilitating mobility‚ and regulating body temperature‚ essential for overall health and quality of life. Understanding its functions is crucial for preventing disorders and improving treatment outcomes.
1.1 Definition and Overview

The musculoskeletal system is a complex system comprising bones‚ muscles‚ joints‚ and connective tissues like ligaments and tendons. It is responsible for enabling movement‚ providing structural support‚ and protecting internal organs. This system works synergistically to maintain posture‚ facilitate mobility‚ and regulate body temperature. Understanding its structure and function is essential for diagnosing and treating disorders‚ as well as promoting overall health and well-being. The musculoskeletal system is a vital component of the human body‚ ensuring proper physical function and stability.
1.2 Importance of the Musculoskeletal System
The musculoskeletal system is essential for enabling movement‚ maintaining posture‚ and providing structural support to the body. It protects vital organs‚ such as the brain and internal organs‚ from external damage. Additionally‚ it plays a role in regulating body temperature and facilitating physical stability. The system’s proper functioning is crucial for performing daily activities and maintaining overall health. Disorders or injuries to this system can significantly impact quality of life‚ emphasizing the importance of maintaining its health through exercise and preventive care.
1.3 Key Components
The musculoskeletal system comprises bones‚ muscles‚ and connective tissues. Bones provide structural support and protection‚ while muscles enable movement through contraction. Connective tissues‚ including ligaments‚ tendons‚ and cartilage‚ stabilize joints‚ facilitate movement‚ and absorb shocks. Ligaments connect bones to other bones‚ while tendons link muscles to bones‚ enabling motion; Cartilage cushions joints‚ reducing friction and preventing wear. Together‚ these components form a cohesive system essential for movement‚ stability‚ and overall bodily functions.
Structure of the Musculoskeletal System
The musculoskeletal system integrates bones‚ joints‚ and muscles‚ with connective tissues like tendons‚ ligaments‚ and cartilage providing stability‚ flexibility‚ and support for movement and body structure;
2.1 Skeletal System
The skeletal system consists of 206 bones‚ forming the body’s internal framework. It provides structural support‚ protects vital organs like the brain and heart‚ and aids in movement by serving as attachment points for muscles. The skeleton is divided into the axial (central) and appendicular (limbs and shoulders) systems. Bones vary in shape and function‚ from long bones in limbs to flat bones like the skull. They also produce blood cells in the marrow and store minerals‚ essential for overall health and bodily functions.
2.2 Muscular System

The muscular system comprises over 600 skeletal muscles‚ accounting for approximately 50% of the body’s weight. These muscles‚ derived from paraxial mesoderm‚ function to facilitate movement‚ maintain posture‚ and regulate body temperature; Skeletal muscles are voluntary‚ while smooth and cardiac muscles operate involuntarily. The system works in conjunction with the skeletal framework to enable motion and support daily activities. Its structure and physiology are vital for mobility‚ stability‚ and overall bodily functions‚ making it an essential component of the musculoskeletal system.
2.3 Connective Tissues (Ligaments‚ Tendons‚ Cartilage)
Connective tissues‚ including ligaments‚ tendons‚ and cartilage‚ play a crucial role in the musculoskeletal system. Ligaments connect bones to stabilize joints‚ while tendons link muscles to bones‚ enabling movement. Cartilage cushions joints‚ reducing friction and absorbing shock. These tissues provide structural support‚ facilitate motion‚ and protect joints from wear. Their integrity is essential for maintaining mobility and preventing injuries. Damage to these tissues can lead to conditions like arthritis or tendonitis‚ highlighting their importance in overall musculoskeletal health and function.
Functions of the Musculoskeletal System
The musculoskeletal system enables movement‚ provides structural support‚ protects internal organs‚ produces blood cells‚ and aids in thermoregulation. These functions are essential for overall bodily function and survival.
3.1 Movement and Mobility
The musculoskeletal system facilitates movement and mobility through the coordinated effort of bones‚ muscles‚ joints‚ tendons‚ and ligaments. Muscles contract and relax to enable voluntary movements‚ such as walking‚ running‚ and lifting. Joints provide flexibility‚ allowing for a range of motions‚ from hinge movements in the knees to rotational movements in the shoulders. This system also enables fine motor skills‚ like writing or gripping objects. Movement is essential for daily activities‚ and its efficiency relies on the integrity of musculoskeletal components‚ making it vital for maintaining independence and quality of life across all age groups.
3.2 Support and Stability
The musculoskeletal system provides structural support and stability to the body. Bones form the framework‚ while muscles and connective tissues work together to maintain posture and balance. This system protects vital organs‚ such as the brain and heart‚ by absorbing shock and distributing forces. Ligaments and tendons add strength to joints‚ ensuring stability during movement. The skeleton acts as an anchor for muscles‚ enabling efficient movement while maintaining the body’s upright position. This dual role of support and stability is essential for daily activities and overall physical function.
3.3 Protection of Internal Organs
The musculoskeletal system plays a critical role in protecting internal organs. Bones‚ such as the skull and ribcage‚ provide a structural shield for vital organs like the brain‚ heart‚ and lungs. Muscles also contribute by offering cushioning and absorbing external forces that could cause harm. Ligaments and tendons add stability‚ preventing excessive movement that might endanger sensitive tissues. This protective function ensures the integrity of organs‚ allowing them to function safely and efficiently within the body. The system’s ability to safeguard vital structures is essential for overall health and survival.

3.4 Blood Cell Production
The musculoskeletal system‚ particularly the skeletal component‚ plays a vital role in blood cell production. Red bone marrow‚ found within the cavities of bones‚ is responsible for hematopoiesis‚ the process of producing blood cells. This includes red blood cells for oxygen transport‚ white blood cells for immune defense‚ and platelets for clotting. The musculoskeletal system’s bone marrow ensures a continuous supply of these essential cells‚ maintaining the body’s ability to function‚ heal‚ and fight infections. This function underscores the system’s importance in overall health and bodily processes.
3.5 Thermoregulation
The musculoskeletal system contributes to thermoregulation by generating and regulating body heat. Muscles produce heat through metabolic activity and shivering‚ helping maintain core temperature. The skeletal system‚ particularly bones‚ acts as insulation‚ reducing heat loss. This function is crucial for maintaining homeostasis‚ especially in varying environmental conditions. Efficient thermoregulation ensures proper cellular function and overall bodily processes‚ highlighting the musculoskeletal system’s role in energy balance and environmental adaptation.
Biomechanics of the Musculoskeletal System
The biomechanics of the musculoskeletal system involves the analysis of forces‚ movements‚ and stability within bones‚ joints‚ and muscles‚ ensuring efficient motion and injury prevention.
4.1 Joint Mechanics
Joint mechanics refers to the study of how joints function‚ involving the interaction of bones‚ ligaments‚ and surrounding muscles. It examines the range of motion‚ stability‚ and the distribution of forces within the joint. Understanding joint mechanics is crucial for diagnosing injuries and improving joint stability. Proper joint function ensures efficient movement and prevents wear and tear‚ which can lead to conditions like arthritis. The alignment and structure of joints play a significant role in overall musculoskeletal health‚ affecting both mobility and the risk of injury‚ and are essential for maintaining posture and facilitating daily activities.
4.2 Muscle Mechanics
Muscle mechanics involves the study of how muscles generate force and facilitate movement. Skeletal muscles‚ controlled by the nervous system‚ contract to move bones at joints. Smooth and cardiac muscles function involuntarily‚ with smooth muscles aiding in processes like digestion and cardiac muscles pumping blood. Understanding muscle mechanics is crucial for analyzing movement patterns‚ preventing injuries‚ and enhancing athletic performance. Proper muscle function ensures efficient force transmission‚ enabling activities like walking‚ running‚ and lifting. Dysfunctional muscle mechanics can lead to injuries or movement disorders‚ highlighting the importance of maintaining healthy muscle structure and function for optimal mobility and overall well-being.
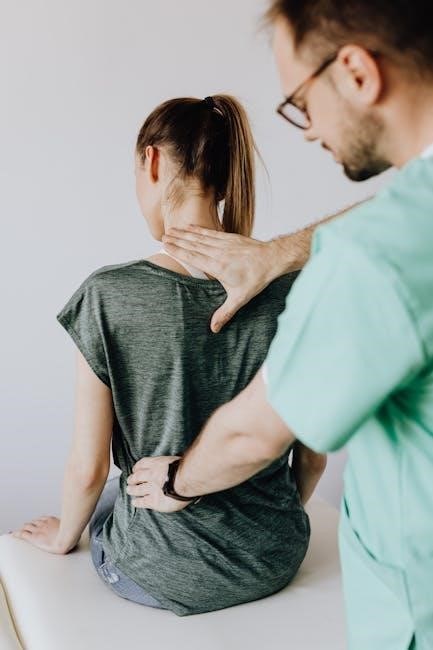

Clinical Significance
The musculoskeletal system’s clinical significance lies in early detection and treatment of disorders‚ improving patient outcomes‚ and managing injuries and degenerative conditions to maintain mobility and quality of life.

5.1 Common Disorders and Injuries
Common musculoskeletal disorders include osteoarthritis‚ rheumatoid arthritis‚ fractures‚ tendinitis‚ and muscle strains. These conditions often result from trauma‚ overuse‚ or degenerative changes. Osteoarthritis affects joints‚ causing pain and limited mobility‚ while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease leading to inflammation. Fractures and sprains are frequent injuries‚ often requiring immobilization or surgery. Tendinitis and muscle strains are linked to repetitive movements or sudden stress. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent long-term disability and improve quality of life‚ particularly in older adults or those with chronic conditions.

5.2 Diagnostic Methods
Diagnosing musculoskeletal disorders involves various imaging techniques and physical examinations. Radiography (X-rays) is commonly used to detect fractures and bone degeneration. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) provides detailed images of soft tissues‚ such as muscles‚ tendons‚ and ligaments. Computed Tomography (CT) scans offer high-resolution bone and joint visuals. Ultrasound is useful for assessing tendon and ligament injuries. Physical exams‚ including range-of-motion tests and palpation‚ help identify pain points and mobility issues. These methods collectively aid in accurate diagnosis‚ guiding effective treatment plans for conditions like arthritis‚ fractures‚ or muscle strains.
5.3 Rehabilitation and Treatment Options
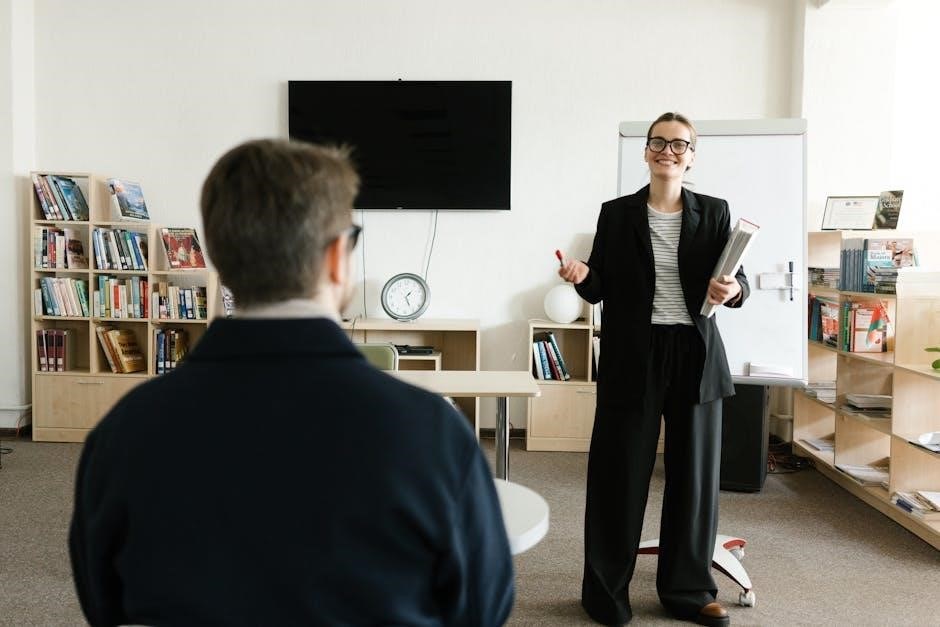

Rehabilitation and treatment of musculoskeletal disorders aim to restore function‚ reduce pain‚ and improve mobility. Physical therapy is a cornerstone‚ focusing on exercises to strengthen muscles and enhance flexibility. Pharmacological interventions‚ such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)‚ are used to manage pain and inflammation. In severe cases‚ surgical interventions like joint replacements or tendon repairs may be necessary. Additionally‚ alternative therapies‚ including acupuncture and chiropractic care‚ can complement traditional treatments. Personalized rehabilitation plans‚ often combining these approaches‚ help patients regain independence and achieve long-term recovery from musculoskeletal injuries or conditions.
The musculoskeletal system is vital for movement‚ support‚ and organ protection. Maintaining its health through exercise and proper care is essential for overall well-being and longevity.
6.1 Summary of Key Points

The musculoskeletal system‚ comprising bones‚ muscles‚ joints‚ tendons‚ and ligaments‚ is essential for movement‚ support‚ and organ protection. It facilitates mobility‚ maintains posture‚ and regulates body temperature. Understanding its structure and function aids in diagnosing and treating disorders. Regular exercise helps maintain muscle strength and bone density‚ crucial for overall health. Proper care and prevention strategies are vital to ensure the system’s longevity and functionality‚ emphasizing its importance in daily activities and quality of life.
6.2 Importance of Maintaining a Healthy Musculoskeletal System
Maintaining a healthy musculoskeletal system is crucial for overall well-being. It prevents disorders‚ enhances mobility‚ and supports daily activities. Regular exercise strengthens muscles and improves bone density‚ reducing the risk of injuries and chronic conditions. Proper care ensures optimal function‚ enabling better posture‚ balance‚ and movement. A healthy musculoskeletal system also boosts longevity and quality of life‚ making it essential to prioritize through physical activity‚ nutrition‚ and preventive measures. This investment in health promotes independence and vitality‚ especially in aging populations.
Related posts:
Discover the comprehensive guide to the musculoskeletal system, covering anatomy, functions, and disorders. Download now!
Posted in PDF
Recent Comments
Archives
- January 2026
- December 2025
- November 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023